Know all the angles.
Empower students to experiment with abstract concepts in their physical surroundings. GeoGebra 3D Calculator enables them to solve maths equations, place a 3D object on a physical surface and even examine it from any angle.

Empower students to experiment with abstract concepts in their physical surroundings. GeoGebra 3D Calculator enables them to solve maths equations, place a 3D object on a physical surface and even examine it from any angle.
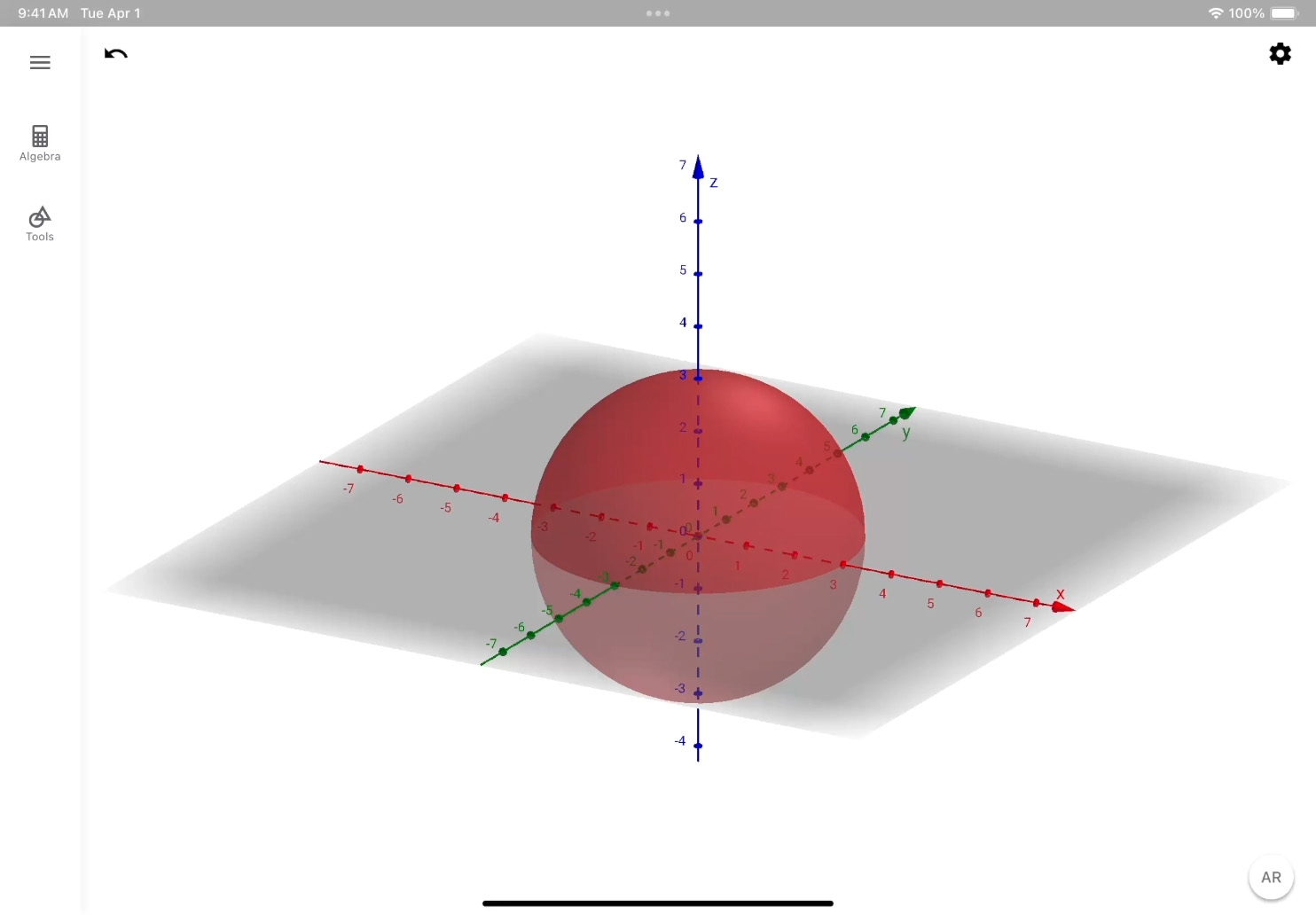
Create a sphere. In the input bar, type the equation x2 +y2 +z2 =9, and tap Enter ![]() . A sphere with the radius of 3 appears in the 3D graphics view.
. A sphere with the radius of 3 appears in the 3D graphics view.
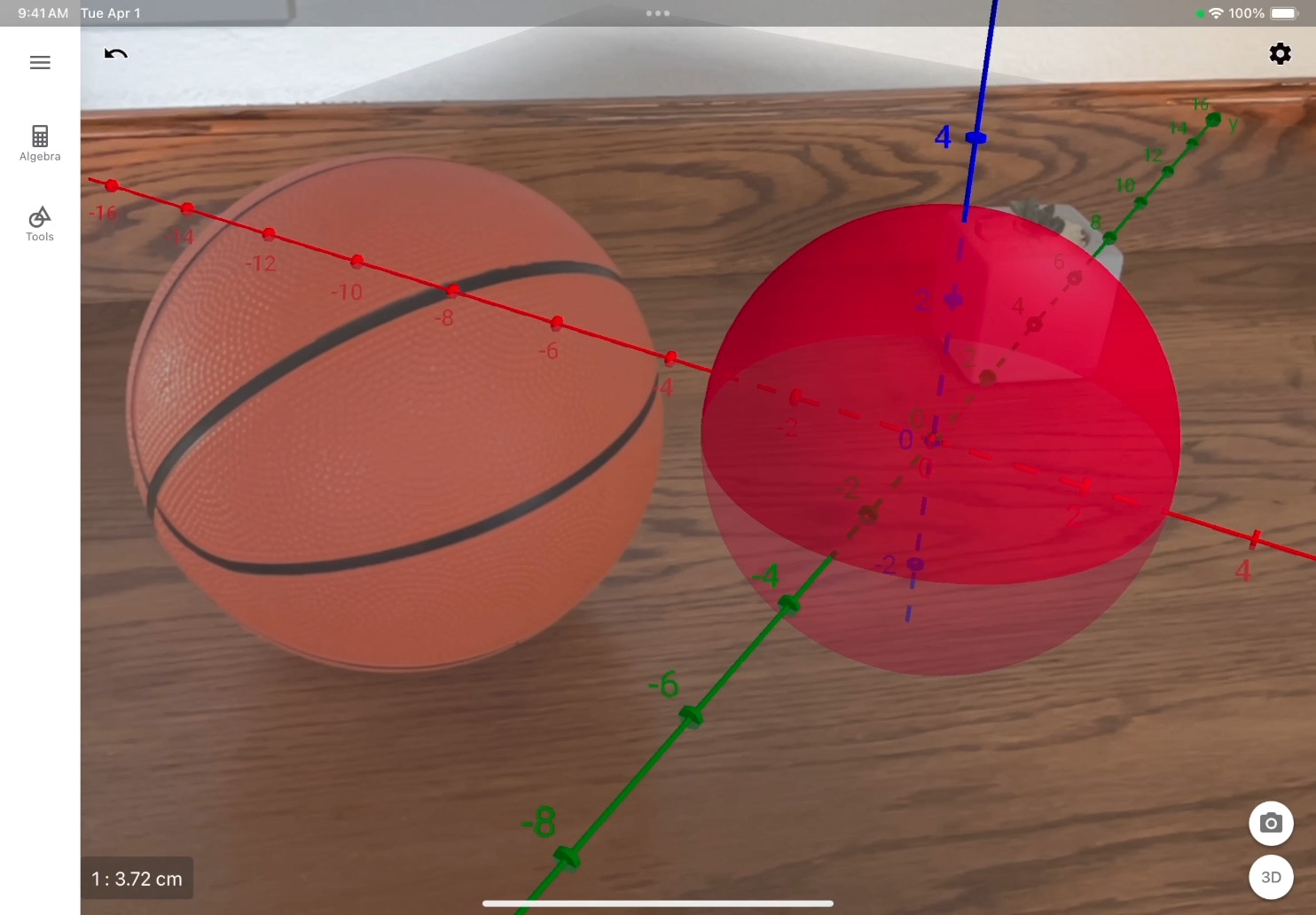
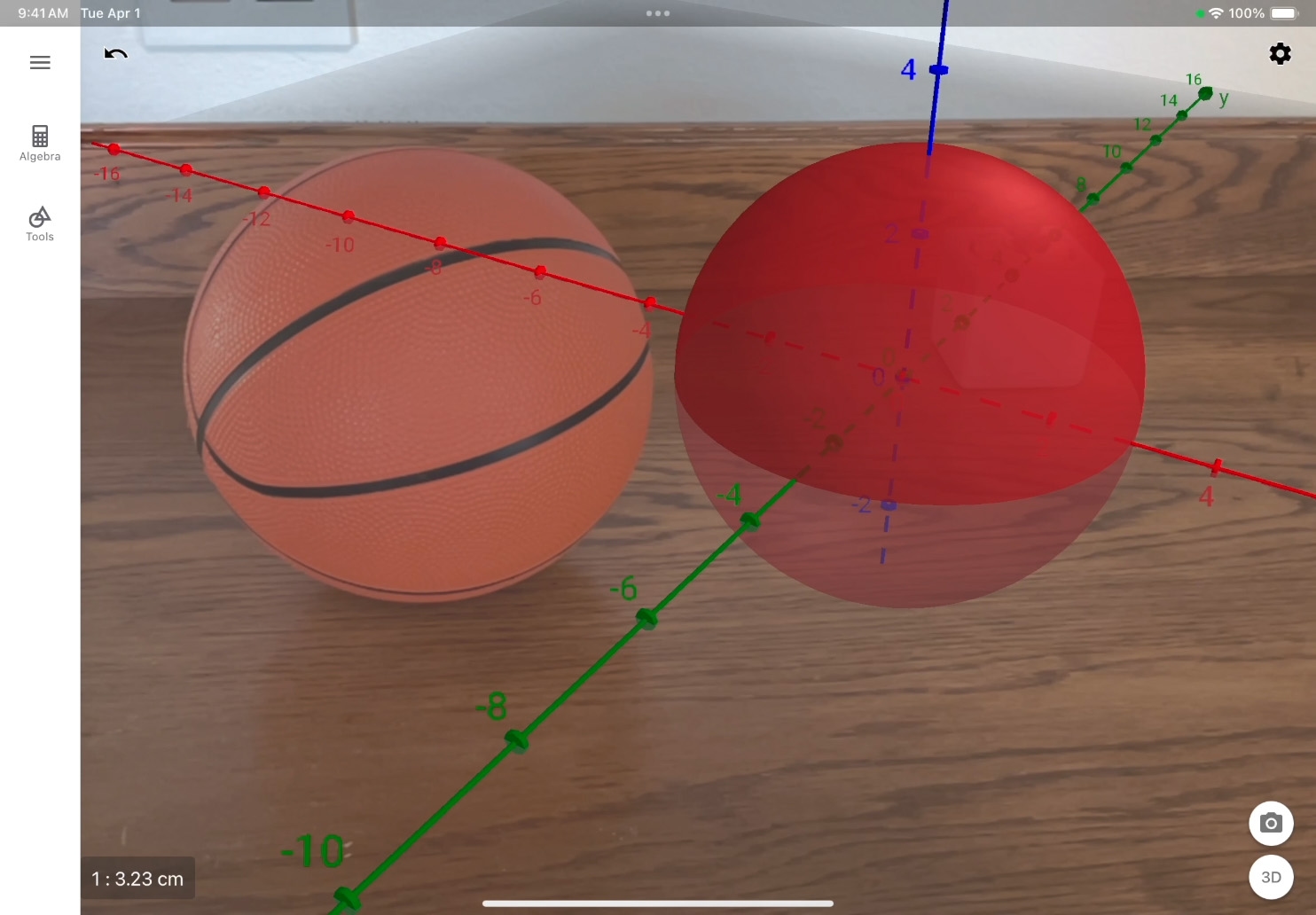
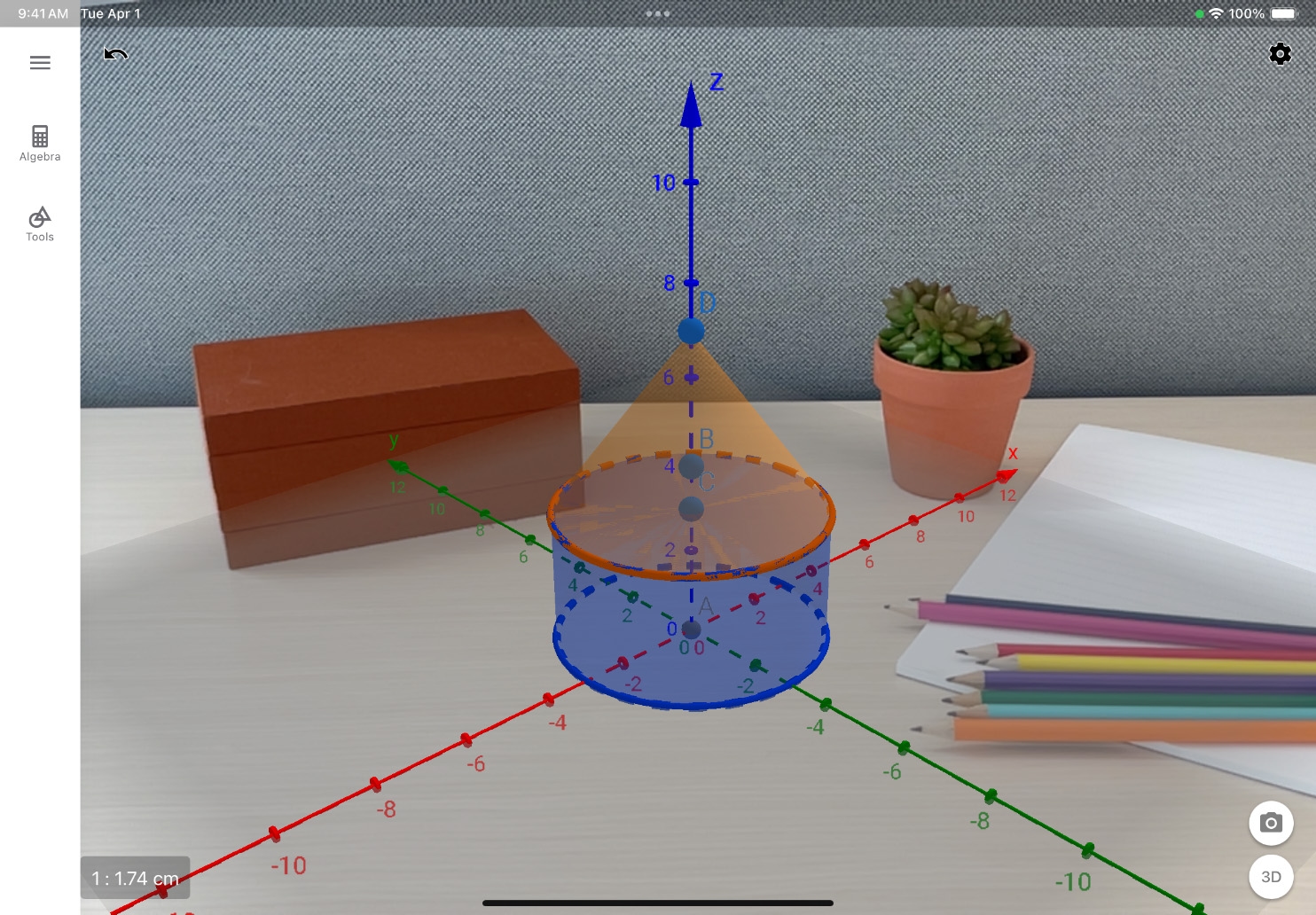
See the sphere in AR. Tap Augmented Reality Mode ![]() to switch modes and follow the onscreen instructions to place the object in the scene.
to switch modes and follow the onscreen instructions to place the object in the scene.
Take a photo. Position the camera so you can see all three axes. Tap Camera ![]() , then tap Save Image from the sharing options.
, then tap Save Image from the sharing options.
Start again. Tap the More menu button, then tap Clear All.
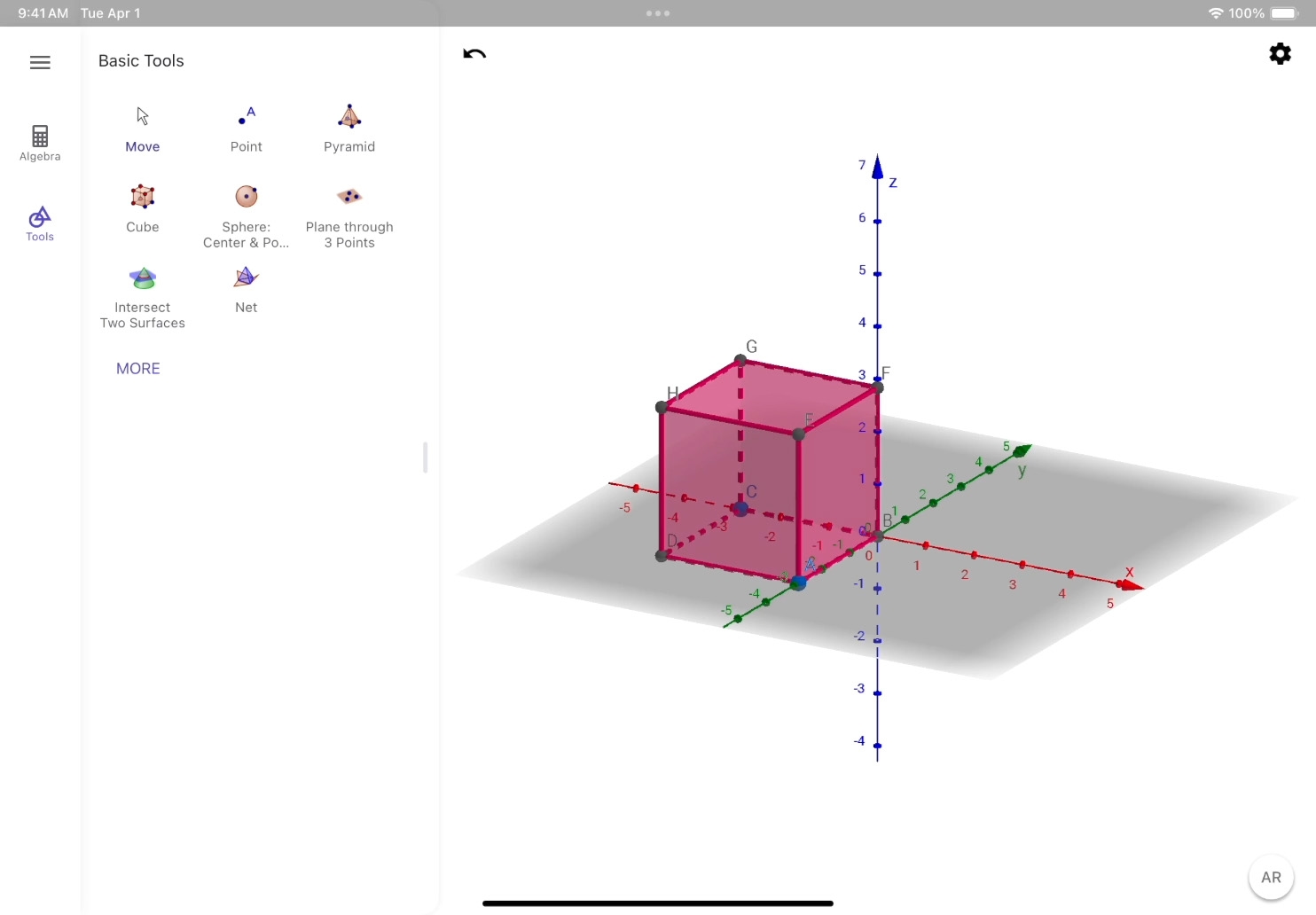
Create a cube. Tap Tools View ![]() and tap Cube Tool
and tap Cube Tool ![]() . Tap the point of origin (0,0,0), and add a second point on the red X–axis.
. Tap the point of origin (0,0,0), and add a second point on the red X–axis.
Change the scale. Switch to AR mode, place the object, then select the Move tool. Pinch and rotate with two fingers to change the scale and angle of the object.
Go further. Create your own objects using the tools from the Tools View ![]() . Then switch to the 3D graphics view by selecting the 3D button
. Then switch to the 3D graphics view by selecting the 3D button ![]() and create your objects there. After creating an object, switch to Augmented Reality Mode
and create your objects there. After creating an object, switch to Augmented Reality Mode ![]() and see it in your space.
and see it in your space.

Gather ordinary objects and categorise them by shape. Use GeoGebra 3D Calculator to recreate the shapes in 3D. In AR mode, take photos of the shapes next to the physical objects.

Explore the geometry of an iconic architectural structure in AR. Choose a well‑known building, such as Fallingwater or the Sydney Opera House, and model parts of the structure to recreate it in 3D.
Explore tried‑and‑tested resources from educators and find fresh ideas to enhance your own lessons.
Visit the ForumLearn more about using AR for teaching and learning, and download all lesson ideas for Augmented Reality in Education.
Augmented Reality Overview
Share what you learnt and help others discover the Apple Education Community.
AR requires an iOS or iPadOS device with iOS 11 and an A9 processor or later.
A link to this page in the Apple Education Community has been copied to your clipboard.